Chapter And Authors Information
Content
Prospects for Innovation in the Technological, Economic and Product Spheres of Insurance in Uzbekistan
Innovations in the technological, economic and product areas of insurance are a complex phenomenon that requires comprehensive study and assessment. There is no single approach to defining innovations in insurance among domestic and foreign researchers. A. N. Zhilkina believes that “insurance innovations assume the presence of such improvement aspects as improving the quality of consumer utility characteristics; scientific and technological novelty; controllability; risk tolerance; cost-effectiveness; efficiency; socio-economic significance; production feasibility; commercial applicability.” (Zhilkina, n.d.). In the studies of M.A. Mirsadykov, it is accepted that innovation is “the profitable use of innovations in the form of new technologies, types of products and services, organizational, technical and socio-economic decisions of a production, financial, commercial, administrative or other nature. In other words, “innovation” is interpreted as the transformation of potential scientific and technological progress into real progress, realized in new products and technologies.” (Mirsadykov, 2010, p. 55).
According to N.E. Savvina “Innovations in insurance are commercial, technical, financial, organizational and social changes in society and the state, leading to creation of a new insurance product. The essence and content of innovations in the insurance business are based on the methodological foundations of innovation theory, taking into account the properties and functions of innovations, laws and patterns of innovation processes, the specifics of innovation management, etc.” (Savvina, 2014, pp. 74-83). Yu.T. Akhvlediani focuses on the fact that “the formation of a modern model for the insurance business development depends on the introduction of modern innovative insurance technologies and the improvement of insurance legislation” (Akhvlediani, n.d.).
In turn, Aksyutina S.V. suggests that “the innovative activities of insurance companies imply a transition to a customer-oriented model of conducting insurance business, internetization of the insurance business, the introduction of new products, the use of digital technologies and new channels in the sale of insurance products and new ways of insurance losses settlement” (Aksyutina, 2020, pp. 395-407).
Summarizing the above, we can assume that innovations in insurance are new insurance products and insurance technologies obtained through the use of scientific ideas and knowledge, improving systems for promoting insurance products and settling insurance claims, and generally improving the system of communications between insurance activities professional participants. Thus, the definition of “innovation in insurance” in this study means the modernization of society and the state leading to changes in existing or developing new insurance product to more fully meet the needs of individuals and legal entities for insurance protection and expanding the use of insurance mechanisms for effective management risks of individuals and legal entities.
Currently, a unique situation has created in Uzbekistan: within comprehensive processes of modernization of the country’s socio-economic sphere, the newest and most advanced communication technologies are being introduced into the daily life of the residents of Uzbekistan. The country’s population is being drawn into the use of new technologies and means of communication, while there is an explosive growth of participants in Internet networks, forums, and online magazines. It should be noted that in the field of insurance services in Uzbekistan, as well as throughout the world, the number of online services is growing; a significant part of potential clients of insurance companies use Internet resources as primary sources of information on insurance services. A survey we conducted among students of the Banking and Finance Academy of the Republic of Uzbekistan revealed that a significant part of potential clients would like to see video presentations of insurance products and services on the websites of insurance companies, and to be able to purchase them.
It should be noted that the Academy participants are middle managers aged from 25 to 40 years old, rather financially secure, mostly family people, who have realized the importance of insurance and want and, what is important, can use the insurance institution as a way of financial protection of themselves and their families from unexpected events. These are those potential policyholders who will buy an insurance policy themselves, if they are interested in something, the priority in working with this group should be the preparation of customer-oriented insurance products and conveying information about it through the Internet and mobile communication to the target audience.
At the present stage of the insurance market development, as some researchers note, the behavioral psychology of financial services potential users, including insurance, is determined by Internet networks and online communication (Sakai, 2011).
These trends in the development of buying behaviors and attitudes, as well as the corresponding reaction to them by the insurance companies, forced to make significant innovations in the field of insurance products themselves and methods of their presentation and sale, cause substantial change in the style of domestic insurers operations. Considering that the country’s population exceeds 36 million people, and the number of small businesses and private entrepreneurship in our country has doubled in recent years, this problem can be effectively solved using big data technologies.
In a broad sense “big data” technology is spoken about as a socio-economic phenomenon associated with the emergence of technological capabilities to analyze huge amounts of data (Viktor Mayer-Shenberger & Kenneth Kuk’er, 2014).
Application of “big data” technology by domestic insurance companies in the processes of collecting, processing and analyzing incoming information gives them competitive advantages, ensures the technologization of basic production processes, and creates a comfortable information environment for potential clients (Big data, 2016). However, the use of “big data” technology leads to significant complication of the data processing process and increases the requirements for the technologies, hardware and software products used for this, and this, in turn, leads to a significant increase in the qualification requirements for employed staff.
The use of “big data” technology in the collection and processing of available information and subsequent analysis of the insurance market state allows us to develop and apply universal algorithms to solve specific problems – identifying development trends in various sectors of the insurance market, establishing the determining factors for the insurance activities efficiency, solving bottlenecks in the domestic insurance business (Milovidov, 2015). The positive role of the state in the insurance development is undoubted, but, as the experience of developed countries shows, such insurance can only achieve high-quality development if private capital predominates in the insurance market. However, at present, the financial possibilities and capital adequacy indicators of a significant part of non-state insurers are limited and do not allow them to invest significant funds in long-term and high-risk innovative projects peculiar to modernized economy. In this regard, innovations in the use of insurance mechanisms to manage the risks of individuals and legal entities are today insufficiently represented.
At the present stage of the domestic insurance market development, the widespread introduction of innovations in insurance activities is prevented by such unresolved issues as: narrow choice of investment instruments available to local insurers to invest temporarily available funds and, as a consequence, low return on investment and limited opportunities for financing innovation; insufficient development level of the insurance market infrastructure, restraining innovative insurance products for a wide range of potential policyholders (small number of channels for promoting insurance services to the population); insufficient number of specialists capable to develop and sell innovative insurance products; low awareness of potential policyholders about advantages of innovative insurance products and, as a result, low demand for them.
Significant risks arise in the activities of the insurer when developing and selling innovative insurance products due to the high degree of uncertainty of the results of this activity, and both positive and negative results from the introduction of innovations are possible, but the positive result can be many times greater than with the usual conducting business.
Insurance products are distinguished according to the innovation degree: insurance products with completely new niche innovations, their number is limited due to their fairly high cost; insurance products with combined innovations (most often these are packaged insurance products combining the advantages of several insurance products in demand); insurance products with “modifying innovations” (improved insurance products previously offered on the insurance market) (Mirsadykov, 2010).
Most often, innovation is carried out in the product area of the insurance market. It is explained by insurance interests changes in the conditions of a modernized economy. In turn, insurance interests’ changes are driven by changes in the socio-economic situation in society.
In the framework of this study, it is accepted that product innovations are aimed at improving the provision of basic services, and technological innovations relate to improving the provision of auxiliary services within the framework of the insurance agreement. Product innovations are carried out by domestic insurers in two ways: insurance company creates a fundamentally new insurance product having consumer qualities that did not exist before with no analogues existing either in domestic or foreign practice; improvement of present insurance product by providing it with new consumer properties. The existing insurance product can be taken from its own practice, the practice of competitors or foreign practice, as well as the practice of providing other financial services.
At the present stage of domestic insurance market development, insurers in most cases use modification of a proven insurance product by giving it new consumer properties and qualities necessary for the effective protection of the property interests of individuals and legal entities in the conditions of modernizing economy.
In Uzbekistan insurance market, innovative insurance products, as a rule, are introduced by leaders and then copied by other market participants. Copying domestic best practices is economically justified – the insurer does not spend money on developing innovations, but simply copies someone else’s positive experience. However, direct copying of advanced innovative insurance products that have proven themselves positively in the foreign markets may not have a positive effect on Uzbekistan insurance market. And, in some cases, it may even lead to a negative result. Borrowing advanced foreign innovative products must be carried out taking into account the local insurers technological effectiveness, the mentality and paying capacity of potential clients of insurance companies.
Widespread application of innovations in the technological, economic and product spheres of insurance is achieved by insurance companies operating on a systematic and comprehensive basis. At the same time, they consider the following main factors as an innovation object: organizational structure of the company; applied technological processes, including strategic and current planning; information support for insurer’s activities; insurance management and insurance marketing. It should be noted that the main points of strategic planning for insurance organization are the definition of a business concept and the development of a mission for its activities.
The introduction of innovations in insurance, as a rule, is a long-term process requiring sometimes significant financing and has a high uncertainty degree. So, the issues of planning innovative activities by the insurer are of particular importance. The implementation of any innovative project passes through the initial (pre-investment) stage, the project implementation stage and the stage of the project completion. For each stage of investment project implementation, the goals and objectives of the stage, the necessary resources and functions of the insurer’s management for the successful implementation of this stage and the investment project as a whole are determined. It is obvious that the success of investment project as a whole depends on how well the initial stage of innovative project implementation was carried out, whether the potential demand for the innovative product was correctly determined, and how well the developed innovative product meets the expectations of insureds.
When planning each stage of the innovation process, several alternatives should be in place for timely consideration of factors changing during the innovation project implementation and ensuring the possibility of successful implementation of a specific stage and the innovation project as a whole. The choice of alternatives should be made taking into account the possibility of original plan revision in case of substantial change of the initial parameters or new or unaccounted risks emergence. The success of the innovation project implementation increases when the insurer’s employees are aware of the goals, objectives and problems arising during the innovative project implementation.
The number of Internet users is rapidly growing in Uzbekistan, creating a potential audience for this sales channel for long-term life insurance. And the implementation of measures aimed at the development of information and communication technologies in the country ensures growth in the number of users of information technologies and their training throughout the republic. In the use of Internet by insurance companies in Uzbekistan (Tsyganov & Bystrov, 2015) the following main approaches are distinguished. Most domestic insurers consider corporate websites solely as an advertising tool – a way to interest a client, attract him to sales points or link insurance agent to him. Although more modern method is to directly sell products online. The scheme is quite simple: the client, having selected the service he is interested in on the company’s website, calculates the price using the built-in web calculator and fills out the application form. The next step is payment, and the insurer delivers the completed documents to the client through an agent or courier or via the Internet. If the product is non-standard, the client sends a formalized request, and experts calculate the insurance price. The advantage for a potential policyholder is also the possibility of feedback from the insurer: you can send an e-mail with a question of interest or call, and payment of the insurance premium can be carried out by simply pressing a key without leaving the monitor. From the point of view of the insurance company, the use of this sales channel can significantly (up to 30%) reduce costs (Kuznetsov, 2005). In addition, online sales are cheaper contrary to agent sales in terms of commission, and also save time for company employees. The website contains complete information about the product reducing the possible number of customer questions. In addition, the insured performs part of the work related to the documents’ preparation in electronic form. It is impossible not to take into account the client’s desire to receive the product without unnecessary effort and minimal time investment. And a client who has a positive experience of purchasing policies via Internet automatically becomes a “recommender,” informing family, friends and acquaintances about the benefits of purchasing, attracting more and more clients.
For insurance company planning to organize sales via Internet, it is necessary to remember psychological factors: most customers, before making a decision to buy product, that is, willingness to pay, prefer direct visual contact with the seller. They want to see what the insurer is like, what kind of office and employees it has. Here brand promotion comes to the fore, and Internet insurance can be effective in companies that have a positive image (brand).
Internet allows to significantly reduce the insurer’s acquisition costs in general and for the agent fees payment in particular (up to 25%), as well as significantly expand the potential clients circle due to economically capable active network users. Due to the fact that insurance product sale using Internet occurs through direct contact between the insurer and the potential policyholder, regardless of his geographic location, provides the insurer with the opportunity to sell its insurance services throughout the republic without additional expenses. Obviously, this increases the possibilities for inclusive insurance intensive implementation and attracting new consumers, including for small insurance companies.
The enormous future potential of this customer service form is evidenced by the fact that in developed countries, more than 20% of insurance policies are currently issued via the Internet (Tsyganov & Bryzgalov, 2018). For example, at the end of 2022, Uzbekinvest Export-Import Insurance Company JSC concluded more than 12 thousand insurance contracts via the Internet, and this number was achieved in 2023 after six months of operations.
Prospects for the National Model Formation of Insurance Protection of Property Interests of Individuals and Legal Entities
The domestic insurance market development strategy, along with ensuring the macroeconomic indicators achievement, should contribute to the insurance culture development in terms of increasing the trust of individuals and legal entities – potential insureds – in professional participants of the insurance market by adapting insurance protection mechanisms to local conditions and the population mentality.
The solution to the above issues can be the implementation of a national model of insurance protection of the property interests of individuals and legal entities. Such a model should ensure effective protection of the property interests of corporate clients, private and small businesses and the population and help improve the insurance culture in the country (Insurance culture refers to the awareness of the necessity of insurance costs and the realization of such expenditures.).
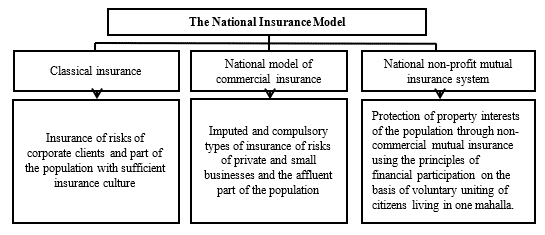
Coverage of the population of the regions and private and small business entities located in the regions by various types of insurance services within the framework of the three-level model of national insurance will mobilize investment opportunities of the regions and will contribute to the development of both regional insurance markets and the insurance market of the Republic as a whole (Figure 6.1).
Figure 6.1. Model of national insurance
Source: Developed by the author on the basis of R. Azimov, 2021, Insurance in Uzbekistan: history, current state, challenges in the process of development, insurance of foreign economic activity, p. 168
As a rule, the risks of corporate clients cannot be placed within one country and are reinsured abroad; therefore, insurance conditions must comply with international rules and regulations of classical commercial insurance. Thus, the national model of insurance protection of the property interests of corporate clients should contain various options for classical commercial insurance.
Imputed and compulsory types of risk insurance for private and small businesses and the wealthy part of the population can be implemented within the framework of modernized classical insurance (with return of the paid insurance premium part), inclusive insurance and commercial mutual insurance.
The relevance of inclusive insurance for Uzbekistan is primarily justified by the scale of the poor population, which at the beginning of 2020 amounted to up to 15% of the total population (Electronic resource: https://www.gazeta.uz/ru/2020/02/27/poverty/ Date of application: 02.02.2022).
According to the Central Bank of the Republic of Uzbekistan, 38.7% of household respondents classified themselves in the group with incomes of 2-4 million Soums per month; the level of well-being of the majority of households remains relatively low, but at the same time technically equipped. On one hand, according to the State Statistics Committee of the Republic of Uzbekistan, in Uzbekistan there are 48 cars per 100 households, households are equipped with televisions, refrigerators, air conditioners and washing machines. 100% of the working population have mobile phones, the provision by personal computers is growing. On the other hand, household property is practically not insured. The situation is similar with personal insurance, this is explained by the fact that the main item of expenditure for these households are the expenses for essential goods and consumer goods.
By the end of 2022, the share of small and private businesses in the republic’s GDP reached 54.9%, in construction it amounted to 72.4%, in the total number of employees – 74.4%. More than 62% of those employed in small businesses in the country are engaged in private entrepreneurship and only about 16% are from small enterprises and micro-firms, which are the main client base of insurance companies; in this case, they mainly turn to insurers to receive compulsory civil liability insurance: motor, employers, carriers and owners of high-risk objects, as well as to buy insurance policies for imputed insurance – collateral property insurance, borrower’s liability insurance, borrower’s life insurance in favor of the bank, and etc. Thus, private and small businesses do not actually use insurance mechanisms as an element of their own risk management system but use insurance as a means to access credit resources. Low financial literacy of representatives of private and small businesses, especially managers of farms and dekhkan farms, and insufficient understanding of the essence of insurance services limits the use of insurance by private and small businesses to protect their property interests.
It should be noted that COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant negative impact on the real incomes of the population, as well as private and small businesses.
The relevance of inclusive insurance is also confirmed by Uzbekistan’s exposure to natural disasters such as mudflows, earthquakes, landslides, avalanches, floods and droughts, which have devastating consequences for the country’s economy and population. Of particular concern is the vulnerability of the rural population to natural disasters in Uzbekistan, as approximately 49.56% (2019) of the population lives in rural areas and is heavily dependent on subsistence agricultural production. Here are just some examples of the negative consequences of natural disasters:
– an earthquake occurred in 1966 in the city of Tashkent caused damage in the amount of 300 million US dollars (equivalent to 10 billion US dollars today);
– 140 billion soums of material damage was caused in Bukhara as a result of strong winds in the spring of 2020.
As noted above, Uzbekistan is also exposed to risks of a technogenic nature – as a result of a water outburst from the Sardoba reservoir, total losses and costs amounted to more than 1.5 trillion soums.
In recent years, various options for inclusive insurance products have been offered in the insurance markets of the Kyrgyz Republic, Turkey, New Zealand and Romania (Table 6.1), and the inclusive insurance option implemented in the Kyrgyz Republic is practically a reincarnation of compulsory property insurance for individuals, carried out by Gosstrakh in the Soviet years. The most successful, in our opinion, option of inclusive insurance was used in Turkey, however, none of the countries listed above managed to achieve full population coverage with inclusive insurance types.
For the widespread use in domestic practice of inclusive types of classical commercial insurance of property interests of private and small businesses and the population, it is necessary to solve the following issues: ensuring effective demand from the population due to the low living standard and increasing the insurance culture level; crucial expansion of sales channels focused on the insurance products sale for inclusive insurance – primarily the retail sales network; improving the professional level of employees of insurance companies involved in the sale of insurance products to the population; develop comprehensive programs combining new and traditional insurance products.
Table 6.1. Insurance markets and inclusive insurance main parameters
|
|
New Zealand |
Romania |
Turkey |
Kyrgyz Republic |
|
Code (name of the inclusive insurance program) |
EQC |
PAID |
DASK (TCIP) |
Mandatory Insurance of Houses against Fire and Natural Disasters |
|
Program type |
Public |
Private |
Public-private |
Public |
|
Number/type of disasters included |
5: Earthquake, natural landslip, volcanic eruption, hydrothermal activity, tsunami |
3: Earthquake, flood, landslide |
1: Earthquake |
18: Earthquake, flood, strong wind, avalanche, hail, and so on. |
|
Insurance form |
Voluntary |
Mandatory |
Mandatory |
Compulsory |
|
Premium: Flat or riskbased |
Flat |
Flat; 2 policy types (depending on type of property |
Ranges by 3 pricing factors (location and type/size of property) |
Flat; different by rural/urban |
|
Premium size |
20 cents per 100 fire insurance cover; capped at $NZ 345 |
1 per 1000 |
0.44–5.50 per 1000 |
1.2 per 1000 |
|
Coverage size |
Maximum $NZ 150,000 |
€10,000 or €20,000 |
Average coverage of about $US60,000 |
$US 7,200 – 14,300 |
|
Assets covered |
Buildings, land |
Buildings |
Buildings |
Buildings |
|
Deductible |
Yes |
No |
Yes, 2% |
No |
|
Reinsurance |
Private and government |
Private |
Private and government |
No access to reinsurance |
|
Claims assessment |
Damage assessment that considers replacement cost |
Damage assessment that considers replacement cost |
Damage assessment that considers replacement cost |
Damage assessment estimating % of affected area |
|
Government role |
Guarantor for when funds are exhausted |
Supports with legal frameworks |
Provides excess of loss reinsurance; supports with favorable legal frameworks |
Supports with legal frameworks |
Source: World Bank Report, 2020
It should be noted that the Uzbekistan population is very poorly covered by inclusive types of insurance; the main share of insurance premiums is generated by legal entities. At the same time, in developed countries, the population plays the most important and fundamental role in shaping the total volume of insurance transactions.
This population attitude towards insurance in general and towards inclusive types of insurance in particular is explained by the lack of trust in insurance organizations, low level of insurance culture and the presence of paternalistic sentiments among its significant part which brings to the conviction that the state is obliged to ensure the protection of their property interests in any cases, as well as insufficient income levels of the population.
The determining factor among the above factors is the population’s distrust in domestic insurance companies and insurance in general.
The reluctance, and in some cases the inability of domestic insurers to systematically and massively engage in insurance of risks of individuals, especially in rural areas, due to the low profitability of these operations also does not contribute to increasing confidence in insurance organizations.
In addition, the lack of trust in insurance protection mechanisms among the population is due to the poor work quality of insurers in settling claims – insurance payments are often delayed or loss is incompletely compensated, and sometimes not compensated at all.
Increased public confidence in insurance will be facilitated by the widespread introduction of insurance mechanisms to protect the property interests of the population related to housing through non-commercial mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation based on a voluntary association of citizens living in the same neighborhood (mahalla).
To implement this option of insurance protection, it is proposed that voluntary quarterly contributions from residents of mahalla (in the amount of 100 thousand Soums for urban residents and 50 thousand Soums for rural residents) are to be accumulated on the balance sheet of mahalla as a separate line in the special insurance fund to protect the property interests related to housing, based on the size of the sum insured of at least one thousand (for the rural population) and at least two thousand (for the urban population) US dollars in national currency equivalent. The amount of insurance premiums and the sum insured may change upward as the incomes and interest of the residents of mahalla grow. Insurance claims payments are carried out on the basis of the decision of a collegial body of a voluntary association of citizens living in the same mahalla. At the same time, the collegial body is headed by the mahalla chairman, and the members of the body are determined by a simple vote of mahalla residents who have paid contributions to the “Sugurta-tez yordam” (“Insurance – Emergency Aid”) special mahalla insurance fund, which is exempt from tax payments. The work of the collegial body is carried out free of charge, and the management of affairs is entrusted to the accountant of the makhala committee.
The funds of the special insurance fund can only be used:
- To pay insurance claim upon the occurrence of insured event;
- Carrying out preventive and depressive measures.
Temporarily available funds from special insurance funds are invested in accordance with the approved provisions. Any capable resident of the mahalla who has made contributions to the special mahalla insurance fund can request and receive information about the accumulation and expenditure of funds from the special insurance fund. Spending of funds from the special insurance fund is carried out on the basis of decisions of the mahalla collegial body, headed by the mahalla chairman.
Thus, the activities of non-profit mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation in the form of a special mahalla insurance fund:
– are not related to making profit as the main goal of its activities, profit can only be obtained from investing temporarily free funds of the fund;
– focused on reducing acquisition and administrative costs;
– information is accessible and open to mahalla residents who paid quarterly contributions to the special mahalla insurance fund;
– is local in nature (within the mahalla), which has a positive effect on the formation of a trusting attitude towards it by the local residents, other organizations and authorities;
– involves the general public in the process of inclusive insurance;
– ensures the insurance culture growth of the population.
Thus, in the economic modernization conditions, the national model of insurance protection of property interests of individuals and legal entities should contain:
– for corporate clients – various options for classic commercial insurance and commercial mutual insurance;
– for imputed and mandatory risk insurance types for private and small businesses and the wealthy part of the population – modernized classic insurance (with the return of paid insurance premium part), inclusive insurance and takaful insurance;
– for insurance protection of property interests of the population related to housing – non-profit mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation on the basis of a voluntary association of citizens living in the same mahalla.
Formation of Insurance Development Strategy Based on the National Insurance Model in Uzbekistan for the Period Until 2030
The formation of effective insurance development strategy is primarily determined by the presence of effective demand, which, in turn, depends on the macroeconomic state – the state and prospects for development of: the country’s economy as a whole; industry and services; the country’s financial system in general and the insurance market in particular, as well as the state social policy.
President of Uzbekistan Sh.M. Mirziyoyev in accordance with the approved “State Program for the Implementation of the Action Strategy for Five Priority Areas of Development of the Republic of Uzbekistan in 2017 – 2021” (Decree of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan, 2017) on August 2, 2019 approved the Decree №4412 “On Measures to Reform and Ensure Accelerated Development of the Insurance Market of the Republic of Uzbekistan” (Resolution of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan, 2019). This resolution identified the following priorities for the domestic insurance market development for the period 2019 – 2022: further transformation of the country’s national insurance market to ensure its dynamic development; meeting the growing needs of individuals and legal entities for reliable insurance protection through the introduction of new types of insurance services and insurance products; increasing the insurance culture level in the country by increasing the confidence of insurance consumers in the activities of insurance market professional participants through the unconditional fulfillment of their obligations under existing insurance agreements.
At the same time, the main directions of reforms and accelerated development of the insurance market of the Republic of Uzbekistan were determined: “improving the insurance sector legal framework, including consistent implementation of standards and recommendations of international organizations and the best global practices in this area; institutional development of the insurance regulation system aimed at ensuring the reliability and sustainability of the insurance market through the introduction of effective regulatory mechanisms and prudential supervision; increasing the capitalization level, solvency and financial stability of insurance market professional participants, improving the quality of their assets, as well as developing the investment activities of insurers; developing and expanding the insurance market infrastructure by intensifying the activities of insurance brokers, improving the work system of insurance agents, introducing bancassurance mechanisms, as well as increasing the role of the insurance market professional participants as a whole; strengthening the protection of the rights of insurance services consumers and other subjects of insurance activities, increasing the insurance literacy of the population and their trust in insurance, ensuring openness and transparency of the insurance market; expanding the volume, range and improving the quality of insurance services provided through the introduction of new innovative and development of traditionally popular insurance products; widespread use of modern information technologies in the field of organizing and regulating insurance activities, active introduction and development of electronic types of insurance services; improving the system of training, retraining and advanced training of insurance market specialists, using modern teaching methods, stimulating research activities in the field of insurance; formation and maintenance of a positive image, as well as increasing the investment attractiveness of the national insurance market, including through its integration into international and foreign insurance markets” (Resolution of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan, 2019).
Realization of target indicators for the insurance market accelerated development in the Republic of Uzbekistan, approved by the above resolution in 2022 compared to 2018, should have ensured increase in: insurance penetration (the share of insurance services in the country’s gross domestic product) by two times; insurance density (insurance premium per capita) by three times; the gross premiums written by more than three times; the total amount of authorized capital in the insurance market by 2.4 times; total assets of insurance organizations in the insurance market by 2.1 times; the total volume of investments of insurance organizations in the insurance market by 2.7 times; the number of insurance services types by 1.7 times; the number of territorial divisions of insurance companies in the regions of the republic by 1.2 times. It is obvious that some of the above indicators at the end of 2022 were not achieved. The main reason for this, along with a number of objective factors, in our opinion, is that the main directions listed above did not include measures to create and further develop effective demand for insurance services among individuals and legal entities.
The strategy proposed in this study was developed on the basis of the analysis of relations between the state, insureds and insurers conducted above, and to a certain extent takes into account the mentality of the people of Uzbekistan and is primarily aimed at forming and developing demand for insurance mechanisms to protect the property interests of individuals and legal entities in conditions of a modernized economy. It should be noted that the proposed strategy is indicative and not imperative; the general goal of the proposed strategy is to create conditions for the insurance mechanisms accelerated development to protect the property interests of individuals and legal entities in conditions of modernization of the republic’s economy through the implementation of a national insurance model in Uzbekistan and the formation on its basis conditions for the development of effective demand among individuals and legal entities for insurance services.
The following goals for the insurance development in the republic are considered as the key goals of the strategy: the use of insurance mechanisms to improve the level and quality of life of individuals in a modernizing economy: promoting economic development by providing affordable insurance mechanisms to manage the risks of legal entities and individuals; creating conditions for the development of insurance culture and insurance in general. The implementation of the proposed strategy is based on the following principles: priority of the interests of individuals and legal entities when using insurance mechanisms to manage their risks; development and realization of measures to develop insurance mechanisms for protecting the property interests of individuals and legal entities in the conditions of a modernized economy; protection of the strategic interests of the domestic insurance market within its integration into regional and global insurance markets; comprehensive development of insurance mechanisms for risk management of individuals and legal entities in market conditions based on partnership and joint responsibility of the state, business and final beneficiaries; transparency and predictability of the development of insurance mechanisms for managing risks of individuals and legal entities in the conditions of a modernized economy. As part of the proposed strategy, the national insurance model includes: classical types of commercial insurance and commercial mutual insurance; modernized types of commercial insurance (inclusive insurance, insurance with participation in the insurer’s profit); non-profit mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation on the basis of a voluntary association of citizens living in the same mahalla.
The main tools for realizing the proposed strategy can be: the development of laws, by-laws, normative and methodological documentation relating to the implementation and operation of the national insurance model, first of all, the project of the Law of the Republic of Uzbekistan “On Mutual Insurance”, normative and methodological documentation on the organization of non-commercial mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation on the basis of a voluntary association of citizens living in the same mahalla; application of soft and indirect regulatory measures to the organization of non-profit mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation on the basis of a voluntary association of citizens living in the same mahalla; strengthening supervision and applying supervisory measures to classic commercial types of insurance and mutual insurance will ensure the legitimacy and protection of the interests of both insurance market professional participants and final beneficiaries; creating infrastructure and ensuring equal access to it when organizing non-profit mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation on the basis of a voluntary association of citizens living in the same mahalla; ensuring information transparency and interaction of the ASB in the implementation of this strategy with professional participants of insurance activities and final beneficiaries reduces uncertainty, influences the behavior and expectations of both insurance activities professional participants and individuals and legal entities.
Important instruments for the insurance development also include increasing the level of financial and insurance education and insurance literacy, which is carried out in order to form the informed choice of insurance mechanisms by individuals and legal entities to protect their property interests.
The insurance development strategy based on the national insurance model in Uzbekistan for the period until 2030, in principle, can be the basis for strategic planning for the long term. If necessary, depending on the planning period, individual aspects of the Strategy can be revised and clarified to ensure the prompt and effective implementation of the goals set in it and the solution of tasks. The instrument for implementing the proposed strategy can be Decrees of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan, Resolutions of the Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Uzbekistan, medium-term documents and road maps of the Ministry of Economy and Finance of the Republic of Uzbekistan, as well as local municipalities, addressing the issues of insurance mechanisms development for protecting the property interests of individuals and legal entities in a modernized economy and containing specific activities indicating the deadlines and names of the parties involved in their implementation. To ensure the strategy consistency with other documents affecting the domestic insurance market development, assessing the progress of the strategy, as well as preparing proposals for updating the strategy, it is advisable for the Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Uzbekistan to form working group with participation of interested parties valid for the strategy duration. Members of the working group can be representatives of ministries and departments, the Central Bank and the State Administration, whose competence includes issues of insurance market development, as well as representatives of the insurance business and the scientific community. The working group must analyze the need to update the strategy at least once a year and submit following report to the Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Uzbekistan. Based on this report, a decision can be made to make changes and additions to the strategy. Separately, it should be noted that the strategy realization requires the presence of qualified specialists capable of working effectively within the framework of the national insurance model. To do this, it is necessary to create insurance training centers between insurance companies for the training and retraining of insurance specialists.
Conclusions on the Sixth Chapter
- Goals of insurance development in Uzbekistan, taking into account the interests of the modernizing economy: maintaining macroeconomic stability in the country by protecting the property interests of the state and business when addressing issues of economic modernization through the use of insurance mechanisms; accelerating the process of transition to a competitive market economy by creating comfortable business conditions through effective risk management for individuals and legal entities; strengthening state regulation of insurance activities in accordance with the standards of the International Organization of Insurance Supervisors, developing mechanisms for self-regulation of insurance activities, strengthening the role of non-governmental non-profit associations and unions of insurance activities professional participants; reducing the risk of social tension in society by ensuring access for the wider population to quality healthcare and education through the use of insurance mechanisms; development of regional insurance by improving the insurance culture of the regional population, as well as owners of private and small businesses located locally through the implementation of a three-tier national insurance model; increasing investment potential by providing access to long-term money through the development of cumulative long-term types of insurance meeting the traditions and mentality of our people, as well as the effective use of temporarily free funds collected in special mahalla funds during the implementation of the national model of non-profit mutual insurance based on the principle of financial co-participation; ensuring the protection of property interests of individuals and legal entities from environmental risks and risks of natural and man-made disasters.
- In conditions of economic modernization, the national model of insurance protection of property interests of individuals and legal entities should contain: for corporate clients – various options for classic commercial insurance; for imputed and compulsory types of risk insurance for private and small businesses and the wealthy part of the population – modernized classic insurance (with the return of the paid insurance premium part), inclusive insurance and commercial mutual insurance; for insurance protection of property interests of the population related to the loss or damage to real estate – non-profit mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation on the basis of a voluntary association of citizens living in the same mahalla.
The main tools for realizing the insurance development based on the national insurance model in Uzbekistan as an element of the risk management system for individuals and legal entities for the period until 2030 can be: the development of laws, by-laws, normative and methodological documentation related to the implementation and operation of the national insurance model, first of all, the project of the Act of the Republic of Uzbekistan “On Mutual Insurance”, normative and methodological documentation on the organization of non-commercial mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation on the basis of a voluntary association of citizens living in the same mahalla; application of soft and indirect regulatory measures to the organization of non-profit mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation on the basis of a voluntary association of citizens living in the same mahalla; strengthening supervision and applying supervisory measures to classic commercial types of insurance and mutual insurance will ensure the legitimacy and protection of the interests of both insurance market professional participants and final beneficiaries; creating infrastructure and ensuring equal access to it when organizing non-profit mutual insurance using the principles of financial co-participation on the basis of a voluntary association of citizens living in the same mahalla; ensuring information transparency and interaction of the ASB in the implementation of this strategy with professional participants of insurance activities and final beneficiaries reduces uncertainty, influences the behavior and expectations of both insurance activities professional participants and individuals and legal entities.





Comments